Oracle Fusion Tax setups
Important Steps to Complete the Tax setups in Oracle Fusion
Tax setups in oracle fusions Started...
2 Types of Taxes in Oracle Fusion
Overview of Transaction Tax:
A tax, that you pay when you buy or sell something in any country that is called the Transaction Tax. As per the Country rule regulation, if we are doing some businesses in that country either doing some sell or purchase something, then we must pay some amount of tax to the country as per the transaction amount and that is called the transaction tax. The amount of Transaction tax on Bill Payments is usually a fixed percentage. Every country has setup their own rates for Transaction Tax. Transaction Tax may vary country to country. Even for Country, there are multiple Transaction tax rates/percentage as pee the Goods and service category.
Overview of Withholding Tax:
A withholding tax , is an income tax to be paid to the government by the payer of the income rather than by the recipient of the income. The tax is thus withheld or deducted from the income due to the recipient. In most jurisdictions, withholding tax applies to employment income. Many jurisdictions also require withholding tax on the payments of Suppliers Invoice Bill’s. In most jurisdictions, there are additional withholding tax obligations if the recipient of the income is resident in a different jurisdiction, and in those circumstances withholding tax sometimes applies to royalties, rent or even the sale of real estate.
Typically, the withholding tax is treated as a payment on account of the recipient's final tax liability, when the withholding is made in advance. It may be refunded if it is determined, when a tax return is filed, that the recipient's tax liability to the government which received the withholding tax is less than the tax withheld, or additional tax may be due if it is determined that the recipient's tax liability is more than the withholding tax. In some cases, the withholding tax is treated as discharging the recipient's tax liability, and no tax return or additional tax is required. Such withholding is known as final withholding.
The amount of withholding tax on income payments other than employment income is usually a fixed percentage.
 |
| Oracle Fusion Tax setups |
Complete Introduction of India GST Transaction Tax in Tax setups in oracle fusion
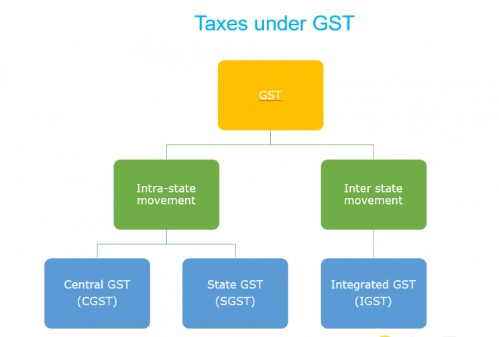
Unlike earlier when there were multiple taxes such as Central Excise, Service Tax and State VAT etc., under GST, there is just one tax. GST is categorized into CGST, SGST or IGST depending on whether the transaction is Intra-State or Inter-State.
To determine whether Central Goods & Services Tax (CGST), State Goods & Services Tax (SGST) or Integrated Goods & Services Tax (IGST) will be applicable in a taxable transaction, it is important to first know if the transaction is an Intra State or an Inter-State supply.
GST Transaction Tax Types: -
- Intra-State supply of goods or services is when the location of the supplier and the place of supply i.e., location of the buyer are in the same state. In Intra-State transactions, a seller has to collect both CGST and SGST from the buyer. The CGST gets deposited with Central Government and SGST gets deposited with State Government.
- Inter-State supply of goods or services is when the location of the supplier and the place of supply are in different states. Also, in cases of export or import of goods or services or when the supply of goods or services is made to or by a SEZ unit, the transaction is assumed to be Inter-State. In an Inter-State transaction, a seller must collect IGST from the buyer.
 |
| Oracle Fusion Tax setups |
Working Example for CGST and SGST:
· Let’s suppose Ravi is a dealer in Maharashtra who sold goods to Rakesh in Maharashtra worth Rs. 10,000. The GST rate is 18% comprising of CGST rate of 9% and SGST rate of 9%. In such case, the dealer collects Rs. 1800 of which Rs. 900 will go to the Central Government and Rs. 900 will go to the Maharashtra Government.
Working Example for IGST:
Consider that a businessman Rajesh from Maharashtra had sold goods to Anand from Gujarat worth Rs. 1,00,000. The GST rate is 18% comprised of 18% IGST. In such case, the dealer has to charge Rs. 18,000 as IGST. This IGST will go to the Centre.








0 comments:
Post a Comment